A dog can pass objects that are smaller than the size of its stool. Dogs have a remarkable ability to pass objects through their digestive system, but there are limits to the size of objects they can safely eliminate.
While it varies depending on the size and breed of the dog, generally, dogs can pass objects that are smaller than the size of their stool. Larger objects can pose a risk of obstruction or choking hazards, which can lead to serious health issues for the dog.
It is essential for dog owners to carefully monitor their pets and keep small objects out of their reach to ensure their safety and well-being.
The Limits Of A Dog’S Digestive System
A dog’s digestive system has limitations in terms of how big an object it can pass. While each dog is different, it is generally recommended to prevent them from ingesting objects that are larger than their mouth or throat to avoid potential complications.
Dogs are known to be curious creatures, often tempted to explore and even taste objects they come across. As pet owners, it’s crucial to understand the limits of a dog’s digestive system to prevent any potential harm or complications. Let’s take a closer look at the anatomy and physiology of a dog’s digestive system and the factors that can affect their ability to pass objects.
Anatomy And Physiology Of A Dog’S Digestive System
The digestive system of a dog is a complex network of organs and processes that work together to break down food and absorb nutrients. Here are the key aspects to consider:
- Mouth and teeth: A dog’s journey through the digestive system begins in the mouth, where they use their teeth to chew and break down food into smaller pieces.
- Esophagus: Once food is chewed and mixed with saliva, it travels down the esophagus, a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.
- Stomach: The stomach plays a vital role in digestion, as it secretes enzymes and acid necessary for breaking down proteins. It also helps sterilize food by killing bacteria and other harmful substances.
- Small intestine: After leaving the stomach, partially digested food enters the small intestine, where most of the absorption of nutrients takes place.
- Large intestine: The large intestine is responsible for absorbing water and electrolytes from the remaining undigested food and eliminating waste through the rectum.
Factors That Affect A Dog’S Ability To Pass Objects
While a dog’s digestive system is designed to handle a variety of foods, there are factors that can impact their ability to pass objects. Consider the following:
- Size and shape of the object: Larger objects or those with irregular shapes may pose a greater challenge for a dog’s digestive system to pass.
- Material composition: Objects that are made of indigestible materials or contain toxic substances can cause blockages or internal injury.
- Dog’s size and breed: Smaller dogs or those with narrow esophaguses may be more susceptible to obstructions.
- Chewing habits: Dogs that are avid chewers or have a tendency to swallow objects quickly are at a higher risk of gastrointestinal issues.
- Preexisting health conditions: Certain underlying health conditions, such as gastrointestinal sensitivity or disorders, can affect a dog’s ability to pass objects safely.
Remember, it’s essential to monitor your dog’s behavior, provide appropriate chew toys, and keep hazardous objects out of their reach. If you suspect that your dog has swallowed an object or is experiencing any digestive discomfort, consult a veterinarian immediately.
By understanding the limits of a dog’s digestive system and taking preventative measures, you can help keep your furry friend safe and healthy.
Common Objects That Dogs Can Normally Pass
Dogs can typically pass objects that are smaller than their throat or that can be safely digested. However, it is important to keep an eye out for small items that may pose a choking hazard.
Dogs are known for their tendency to chew on things, but sometimes they may take it a step further and attempt to swallow objects. While it’s always best to keep dangerous items out of reach, there are some common objects that dogs can comfortably handle.
In this section, we’ll explore some small-sized items that dogs can easily pass without any issues.
Small-Sized Items That Dogs Can Easily Pass:
- Rubber balls: Dogs love playing fetch, and rubber balls are a popular choice. The small size of these balls allows dogs to hold them in their mouths without any difficulty.
- Plush toys: Soft and cuddly plush toys are a favorite among dogs. Since they are usually small in size, dogs can easily chew on them without risking ingestion.
- Bones and rawhide chews: Dogs have a natural instinct to chew, and bones and rawhide chews provide a great outlet for this behavior. These treats are designed to be safe for dogs to chew on and pass through their digestive system.
- Small treats: Dog treats come in a variety of sizes, and smaller treats are generally easy for dogs to eat and digest. Whether it’s a biscuit or a chewy treat, dogs can handle these small-sized goodies without any trouble.
- Small sticks: Dogs love to chew on sticks, and as long as they are small enough, they can pass through a dog’s digestive system without causing any issues.
- Small cloth items: Socks, gloves, or small pieces of fabric may accidentally find their way into a dog’s mouth. While it’s always best to prevent dogs from chewing on clothing or other cloth items, small-sized pieces can pass through their system without much trouble.
Dogs can comfortably handle a variety of small-sized items without any adverse effects. However, it’s essential to ensure the safety of your furry friend by preventing them from ingesting objects that may pose a choking hazard or cause digestive issues.
Potential Risks And Consequences Of Dogs Swallowing Large Objects
Dogs swallowing large objects can lead to potential risks and consequences. The size of the object plays a crucial role in whether a dog can pass it or not, as larger objects may cause blockages in their digestive system, requiring immediate veterinary attention to prevent further complications.
Dangers Of Ingesting Large Objects
When it comes to dogs, we all know they have a tendency to put just about anything in their mouth. From small toys to household items, dogs are notorious for swallowing things they shouldn’t. But what happens when a dog ingests a large object?
The consequences can be quite serious. In this section, we will explore the potential risks and dangers associated with dogs swallowing large objects.
- Obstruction of the digestive system: One of the major risks of a dog swallowing a large object is that it can cause an obstruction in their digestive system. This can happen if the object gets stuck in the esophagus, stomach, or intestines. An obstruction can lead to a range of health problems and complications.
- Gastrointestinal (GI) perforation: Another danger of ingesting a large object is the risk of perforation in the GI tract. Sharp objects or objects with rough edges can potentially puncture through the delicate lining of the esophagus, stomach, or intestines, causing a perforation. This can lead to infection, pain, and in severe cases, can even be life-threatening.
- Choking hazard: Large objects can also pose a choking hazard for dogs. If the object becomes lodged in the throat, it can block the airway and prevent the dog from breathing. Choking is a serious emergency that requires immediate veterinary intervention.
- Toxicity: Some large objects, such as certain household items or plants, may contain toxic substances that can be harmful to dogs if ingested. Swallowing these objects can lead to poisoning and require immediate medical attention.
Potential Health Issues And Complications
Swallowing large objects can have various health issues and complications for dogs. Here are some potential consequences to be aware of:
- Lacerations and damage: Large objects with sharp edges can cause lacerations and damage to the digestive system, including the throat, esophagus, stomach, or intestines. These injuries can lead to pain, bleeding, and infection.
- Digestive system blockages: When a large object becomes lodged in the digestive system, it can block the normal flow of food, liquids, and waste. This obstruction can cause vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, and weight loss.
- Inflammation and infection: Swallowing large objects can cause inflammation and infection in the digestive system. The foreign object can irritate the tissues, leading to inflammation and the potential for infection to develop.
- Surgical intervention: In severe cases, where the object cannot pass naturally or poses a significant risk to the dog’s health, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery may be required to remove the object and repair any damage caused.
- Long-term complications: Depending on the size and nature of the object swallowed, long-term complications may arise. These can include scarring and strictures in the digestive system, which can lead to recurring issues and require ongoing management.
It is crucial to be mindful of the potential dangers and risks associated with dogs swallowing large objects. If you suspect that your dog has ingested something they shouldn’t have, it is important to seek veterinary assistance immediately. Prompt action can help prevent further complications and ensure the well-being of your furry friend.
Signs And Symptoms Of Obstruction Or Blockage
Obstruction or blockage in dogs can lead to various signs and symptoms. It is important to be aware of what objects dogs can safely pass to prevent any potential risks or complications.
Recognizing Signs Of An Object Lodged In The Digestive Tract
When a dog ingests an object that is too large to pass through their digestive tract, it can lead to an obstruction or blockage. As a responsible dog owner, it is essential to be observant and recognize the signs and symptoms of this condition.
By promptly identifying the problem, you can seek veterinary help and potentially prevent further complications. Here are some common indications that your dog might have an object lodged in their digestive tract:
- Vomiting: One of the most noticeable signs of blockage is recurrent vomiting. If you observe your dog vomiting repeatedly and there doesn’t seem to be any other explanation, such as a change in their diet, it may be an indicator of an obstruction.
- Loss of appetite: Dogs with an object blocking their digestive system often lose interest in eating or may completely stop eating altogether. If your dog suddenly refuses to eat or shows a significant decrease in their appetite, it could be a sign of blockage.
- Abdominal pain: Obstruction in the digestive tract can cause discomfort and pain in dogs. They may exhibit signs of abdominal distress, such as whining, restlessness, or a hunched posture. If you notice your dog behaving unusually and showing signs of discomfort, it’s necessary to be attentive and consider the possibility of blockage.
- Diarrhea or constipation: Blockage may disrupt the normal bowel movements of your dog. Diarrhea can occur as the digestive system tries to eliminate the object, while constipation may be an indication that the object is causing a blockage and preventing the passage of stools.
- Straining during elimination: A dog with an object lodged in its digestive tract may exhibit difficulty or straining while attempting to defecate. This can be accompanied by frequent trips to the bathroom without producing stool or producing only small amounts.
If you notice any of these signs or a combination of them, it is crucial to seek veterinary assistance promptly. In many cases, an object trapped in the digestive tract requires professional help to remove it safely and prevent further complications.
Remember, early recognition and treatment can make a significant difference in your dog’s health and well-being.
Common Symptoms Of Blockage In Dogs
When a dog has an object lodged in its digestive tract, it can lead to various symptoms that indicate blockage. Understanding these common symptoms can help you determine whether your furry friend needs medical attention. Here are some signs to be aware of:
- Vomiting: Recurrent vomiting is a key symptom of blockage and should never be ignored. If your dog is vomiting, especially if it includes undigested food or blood, it’s important to seek veterinary care.
- Loss of appetite: Disinterest in food or a sudden decrease in appetite can be a sign that your dog is experiencing digestive blockage.
- Abdominal pain: Dogs in pain may display restlessness, whimpering, or abnormal postures such as a hunched back.
- Diarrhea or constipation: Blockage can lead to irregular bowel movements. Dogs may experience bouts of diarrhea in an attempt to flush out the obstruction, while others may become constipated due to the blockage preventing normal bowel movements.
- Straining during elimination: Struggling to defecate or passing only small amounts of stool, despite frequent attempts, can indicate a blockage in the digestive tract.
If you observe any of these symptoms in your dog, it is essential to contact your veterinarian. Identifying and addressing a blockage promptly can prevent complications and ensure your dog’s wellbeing.
Treatment And Interventions For Dogs With Obstructions
Dogs with obstructions may require various treatments and interventions depending on the size of the object. Proper care should be taken to identify the size limits of objects that a dog can pass to ensure their safety and well-being.
When our furry friends accidentally ingest something they shouldn’t, it can lead to potentially dangerous obstructions in their digestive system. As responsible dog owners, it’s crucial to understand the appropriate treatment and interventions for dogs facing these obstructions. Whether it’s seeking veterinary assistance or considering surgical and non-surgical solutions, let’s explore the options available to ensure our canine companions receive the care they need.
When To Seek Veterinary Assistance
Recognizing the signs of an obstruction and promptly seeking veterinary assistance can be crucial in preventing further complications for our dogs. Here are a few instances when it’s essential to consult a veterinarian:
- If your dog is experiencing persistent vomiting, especially if it contains blood or bile.
- If your dog shows signs of abdominal pain or discomfort, such as restlessness or reluctance to move or be touched.
- If there is a decrease or complete loss of appetite, along with other symptoms like lethargy or dehydration.
- If your dog has difficulty defecating, with signs of straining or producing only small amounts of stool.
- If you suspect that your dog has ingested something potentially hazardous, such as sharp objects, toxic substances, or large foreign bodies.
Seeking veterinary assistance promptly when these signs appear can play a vital role in the dog’s recovery and overall well-being.
Surgical And Non-Surgical Interventions For Obstruction
Treating obstructions in dogs often involves a combination of medical interventions, supportive care, and in more severe cases, surgical procedures. Let’s explore some of the common treatments and interventions for dogs facing obstructions:
Non-surgical interventions:
- Fluid therapy: Administering intravenous fluids helps to rehydrate dogs and correct electrolyte imbalances caused by vomiting or diarrhea.
- Medications: Depending on the specific condition, medications such as anti-emetics (to reduce vomiting) or laxatives (to promote bowel movement) may be prescribed.
- Dietary changes: Adjusting the dog’s diet temporarily, such as providing easily digestible foods or a special prescription diet, can help alleviate gastrointestinal distress.
Surgical interventions:
- Endoscopy: This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a long, flexible tube with a camera into the digestive tract to locate and remove the obstruction.
- Exploratory laparotomy: In more severe cases, a surgical exploration of the abdomen may be necessary to identify and remove the obstruction manually.
- Bowel resection: If the obstruction has caused significant damage or necrosis to a section of the intestine, a surgical removal of the affected portion may be required.
Both surgical and non-surgical interventions aim to restore the normal flow of the digestive tract and alleviate any discomfort or complications caused by obstructions.
Remember, every case is unique, and treatment options may vary depending on the specific circumstances. Consultation with a veterinarian is crucial to determine the most appropriate course of action for your furry friend.
By being vigilant, recognizing the signs of obstruction, and promptly seeking veterinary assistance, we can ensure our dogs receive the necessary treatment and interventions to overcome these challenges. Remember, a well-informed and proactive approach can make all the difference in helping our four-legged friends lead happy, healthy lives.
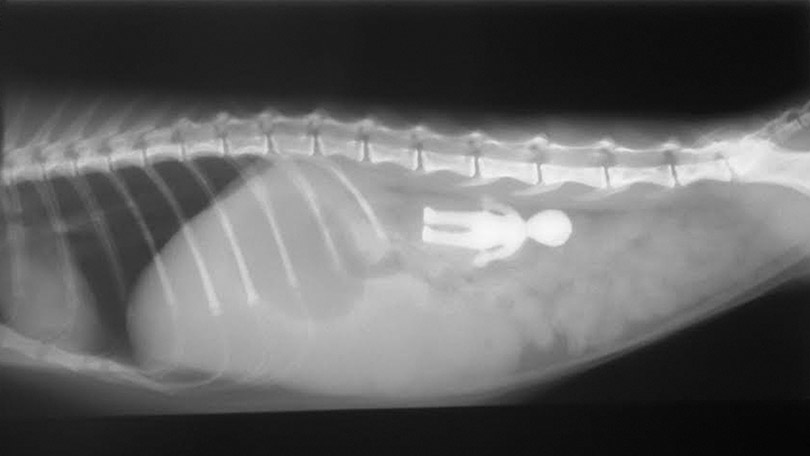
Credit: www.oldstonevets.com
Precautions And Preventive Measures
Taking precautions and preventive measures is crucial when it comes to the size of objects dogs can pass. Understanding a dog’s oral anatomy and keeping small objects out of reach can prevent potential choking hazards or foreign body obstructions. Stay vigilant and ensure your furry companion’s safety by being proactive in dog-proofing your home.
To ensure the safety of your furry friend and prevent them from swallowing large objects, there are some important precautions and preventive measures you can take. By dog-proofing your home and implementing these tips, you can minimize the risk of your dog ingesting something they shouldn’t.
Here are some effective methods:
Dog-Proofing Your Home:
- Keep small objects out of reach: Dogs are naturally curious, so it’s essential to ensure that any small objects, such as buttons, coins, or small toys, are stored away in a secure location.
- Secure trash bins: Dogs are notorious for rummaging through trash bins, which can result in them swallowing harmful items. Make sure your trash bins have tight-fitting lids or are kept in cabinets.
- Close toilet lids: Dogs may be tempted to drink or play in the toilet bowl, which can lead to potential ingestion of harmful cleaning chemicals. Keep toilet lids closed to prevent this from happening.
- Store medications safely: Medications, both prescription and over-the-counter, should be stored in a secure cabinet or high-up location where your dog cannot reach them.
Tips For Preventing Dogs From Swallowing Large Objects:
- Choose appropriate toys: When selecting toys for your dog, make sure they are safe and specifically designed for dogs. Avoid toys with small parts that can easily be chewed off and swallowed.
- Supervise playtime: Monitor your dog while they are playing with toys to ensure they do not bite off and swallow any parts. If you notice any signs of damage to the toy, replace it immediately.
- Properly discard broken toys: Regularly inspect your dog’s toys for any signs of damage. If a toy is broken or damaged, discard it immediately to prevent your dog from potentially swallowing any small or sharp parts.
- Use puzzle toys and treat dispensers: Engage your dog’s mind and provide mental stimulation with puzzle toys and treat dispensers. This can help redirect their focus from chewing on inappropriate objects.
By implementing these precautions and preventive measures, you can create a safer environment for your dog and reduce the risk of them swallowing large objects. Remember, it’s always better to be proactive and prevent such incidents rather than dealing with the potential consequences.
Stay mindful and keep your four-legged friend safe!
Frequently Asked Questions On How Big An Object Can A Dog Pass?
How Big Of An Object Can A Dog Pass?
Dogs have the ability to pass objects that are smaller than their throat diameter to avoid choking hazards.
What Objects Can Dogs Typically Pass?
Dogs can typically pass objects such as toys, small bones, and digestible treats without any issues.
Can Dogs Pass Large Objects?
No, dogs cannot pass large objects as they can cause blockages in their digestive system and lead to serious health problems.
What Are The Risks Of A Dog Swallowing Large Objects?
Swallowing large objects can lead to choking, intestinal blockages, or even surgery to remove the object.
How Can I Prevent My Dog From Swallowing Large Objects?
It’s important to supervise your dog during playtime and avoid giving them access to objects that are too big for them to swallow.
What Should I Do If My Dog Swallows A Large Object?
If your dog has swallowed a large object, contact your veterinarian immediately for guidance and possible treatment options.
Conclusion
It is clear that the size of objects a dog can pass largely depends on their breed, size, and individual characteristics. While some dogs may have a remarkable ability to pass relatively large objects without complications, it is always important to prioritize their safety and well-being.
As caring pet owners, we should be vigilant in keeping small objects out of their reach to prevent choking hazards or intestinal blockages. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and providing appropriate toys can help ensure their physical and mental stimulation without risking their health.
Remember, dogs are curious creatures, and it is our responsibility to create a safe environment where they can thrive. By understanding the limits of what our dogs can pass and taking the necessary precautions, we can enjoy a harmonious bond with our furry friends for years to come.
Last Updated on May 10, 2025 by Pauline G. Carter

